Try Hack Me | Carnage Writeup
Foreword.
This is a writeup of the carnage challenge from the Try Hack Me website. Basically it’s a blue team challenge on the analysis of a C2 Cobalt Strique installation and communication system.
Introductions.
The objective of this challenge is to analyze and understand the functions and behavior of a Command and Control Cobalt Strike.
The tools used will be the following
Q1 : What was the date and time for the first HTTP connection to the malicious IP?
filter by http in wireshark
Wrieshark Filter - http
Awnser: 2021-09-24 16:44:38
Q2 : What is the name of the zip file that was downloaded?
On wireshark we can see the elements downloaded or manipulated via HTTP. And this via the following path.
File -> Export Objects -> HTTP
once in this window, we filter by filename, and we get the unique zip document.
Awnser: documents.zip
Q3 : What was the domain hosting the malicious zip file?
In the same place as the previous question (http export), you can see the hostname linked with the filename.
Awnser: attirenepal.com
Q4 : Without downloading the file, what is the name of the file in the zip file?
By double clicking on the document.zip field in the HTTP Export section of the previous questions, Wireshark takes us directly to the location of the packet.
Then you have to follow the content of the HTTP stream (Right click on packet -> Follow -> HTTP Stream).
Here we can see the raw content of the HTTP transmission. And we can see the name of the file contained in document.zip
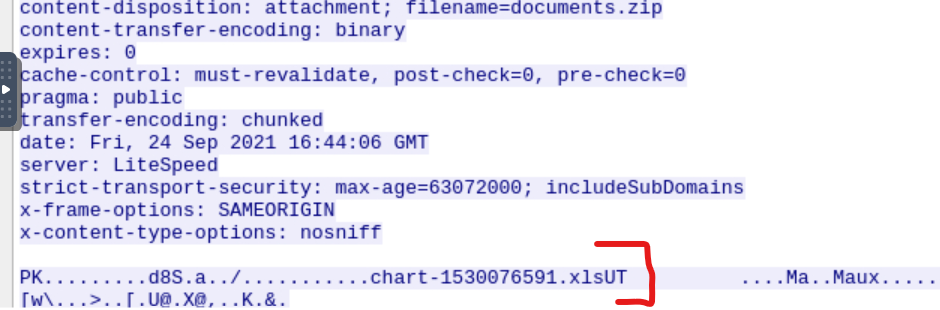
Awnser: chart-1530076591.xls
Q5 : What is the name of the webserver of the malicious IP from which the zip file was downloaded?
Still staying in the previous flow, we can analyze one of the HTTP packets.
There is information related to the HTTP section of the TCP packet that we can analyze to solve this challenge. Here the section that interests us is server.
Awnser: LiteSpeed
P.S:
the server field is only visible when downloading the file, so you have to analyze the http packet that has the server’s ip as its source, not the victim’s.
Q6 : What is the version of the webserver from the previous question?
On the same packet as the previous questions, in the filed x-powered-by you can see the PHP versions that powered the webserver.
Awnser: PHP/7.2.34
Q7 : Malicious files were downloaded to the victim host from multiple domains. What were the three domains involved with this activity?
For this question, it is necessary to make a small state of the existing.
The malleable document was uploaded on September 24, 2021 at 16:44:06, so the infection can only start from that moment.
The connections Cobalt strike, are done via https, thus via a communications ssl.
| We avony here two filter that we can apply to brim (ssl | sort() by ts). |
Filter by ssl and date . take in count 1 minute for the time the connexionx can be made and start see the interactions made in 16:45:06
Brim filter:
_path==”ssl” id.resp_p 443 cut ts,server_name sort ts
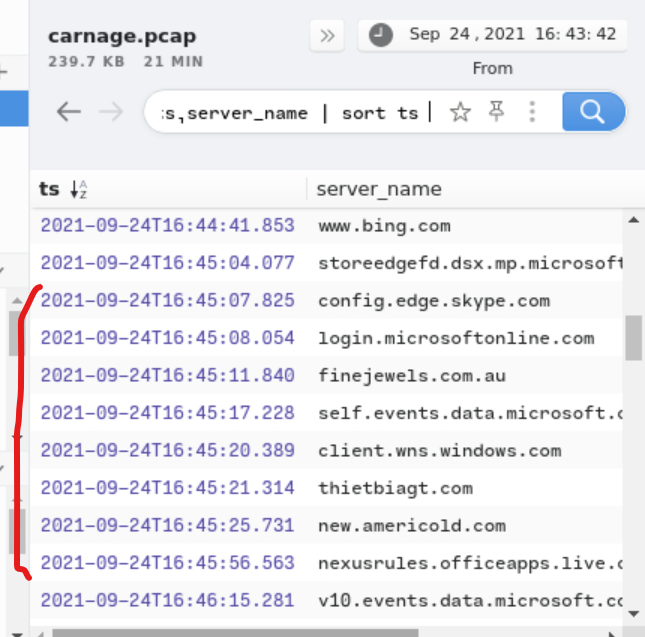
after that use virus total to detect if the server_name is register or know to host the chart.xls file.
tree host detected
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/domain/thietbiagt.com/relations
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/domain/finejewels.com.au/relations
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/domain/new.americold.com/relations
Awnser: finejewels.com.au, thietbiagt.com, new.americold.com
P.S:
Q8 : Which certificate authority issued the SSL certificate to the first domain from the previous question?
By adding the issuer field to the Brim filter of the previous question we can see the organization that issues the certificates.
| Brim filter: _path==”ssl” | id.resp_p 443 | cut ts,server_name,issuer | sort ts |
Awnser: GoDaddy
Q9 : What are the two IP addresses of the Cobalt Strike servers? Use VirusTotal (the Community tab) to confirm if IPs are identified as Cobalt Strike C2 servers. (answer format: enter the IP addresses in sequential order)
on this questions , one ip is harder to find. the fisr one can be found with this idea.
We know that CB server can have some suspicious behavior (alert). We also know that the HTTPS traffic is encryoted (ssl).
And finally that a C2 normaly make more than a couple connextions.
so with that in mind we can make the following filter in brim.
Brim filter:
_path==”ssl” alert sort ts uniq cut id.resp_h count() by id.resp_h sort -r count
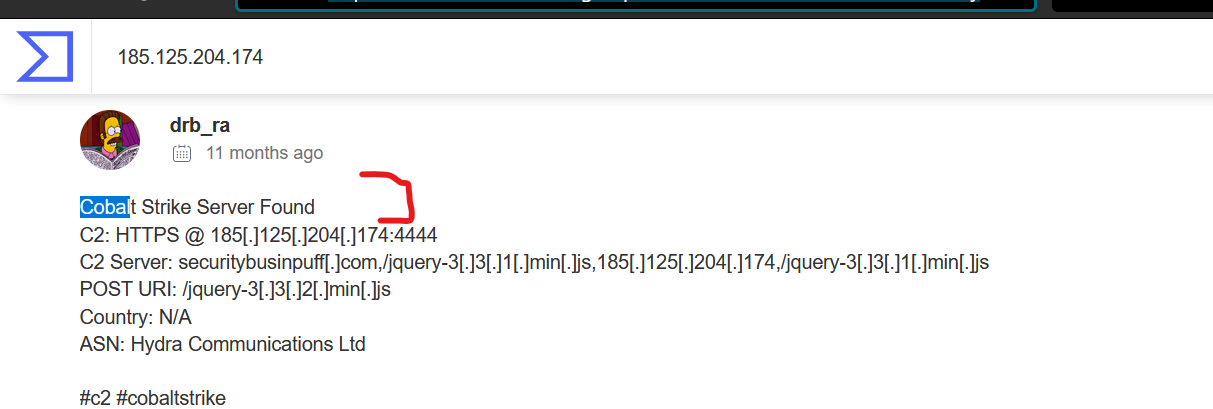
We test the first IP on virus total , and see in the comminity sections.
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/ip-address/185.125.204.174/community
I found the second one out of a guess, i guess that the second C2 server will share one first 8bytes of their IP.
So i tried this filter in brim.
cut id.resp_h sort id.resp_h uniq
and i tried all the IP that start with 185.
Awnser: 185.106.96.158, 185.125.204.174
Q10 : What is the Host header for the first Cobalt Strike IP address from the previous question?
In wireshark filter the ip and follow the firrst HTTP flux, go on the host field
Awnser: ocsp.verisign.com
Q11 : What is the domain name for the first IP address of the Cobalt Strike server? You may use VirusTotal to confirm if it’s the Cobalt Strike server (check the Community tab).
Check again the same type of post that in question 9.
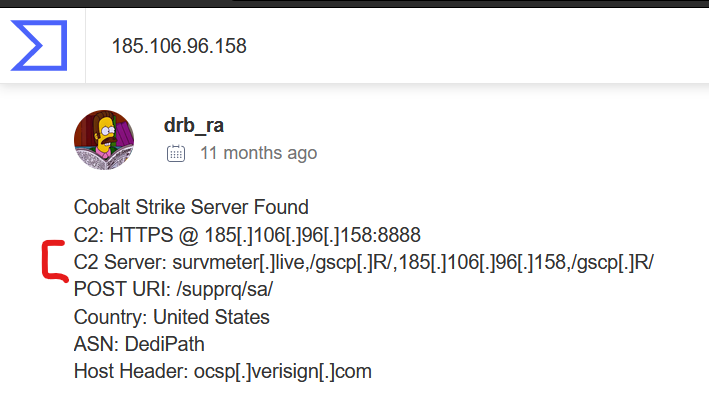
Awnser: survmeter.live
Q12 : What is the domain name of the second Cobalt Strike server IP? You may use VirusTotal to confirm if it’s the Cobalt Strike server (check the Community tab).
Do the same thing that in the previous question.
Q13 : What is the domain name of the post-infection traffic?
In the export HTTP sections of wireshark multiple and some wierd interactions occure , and evry time its connected with maldivehost.net , by tring out this domain name in virus total, we found the C2 post exploit server.
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/domain/maldivehost.net
Awnser: maldivehost.net
Q14 : What are the first eleven characters that the victim host sends out to the malicious domain involved in the post-infection traffic?
In wireshark select tyhe first packet in EXPORT HTTP and follow the first HTTP packet.
tha field that interest us is the POST field
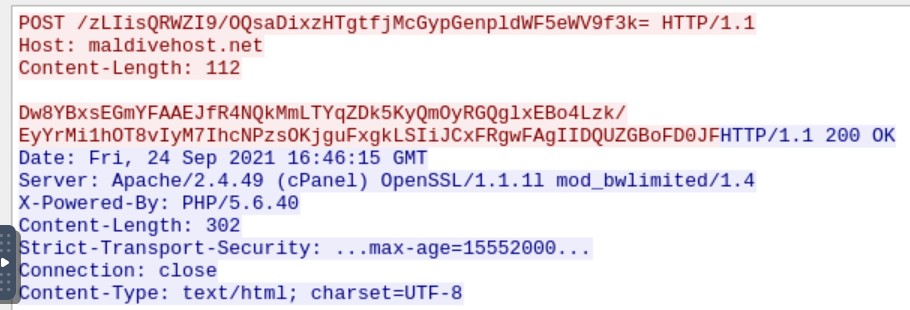
Awnser: zLIisQRWZI9
Q15 : What was the length for the first packet sent out to the C2 server?
Go back to the HTTP packet and watch the lenght field
Awnser: 281
Q16 : What was the Server header for the malicious domain from the previous question?
go back to the capture taken in questions 14 and watch the server field.
Awnser: Apache/2.4.49 (cPanel) OpenSSL/1.1.1l mod_bwlimited/1.4
Q17 : The malware used an API to check for the IP address of the victim’s machine. What was the date and time when the DNS query for the IP check domain occurred? (answer format: yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss UTC)
for this one , we know that a api is use and that the DNS protocole is involved. so by tring this filter on brim.
_path==”dns” api cut query, ts
We found the following.
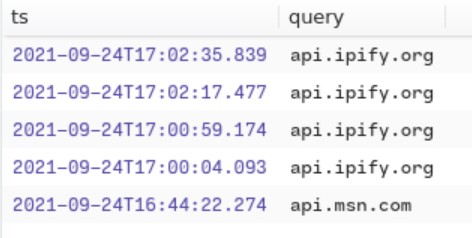
Awnser: 2021-09-24 17:00:04
Q18 : What was the domain in the DNS query from the previous question?
the awnser is in the previous capture.
Awnser: api.ipify.org
Q19 : Looks like there was some malicious spam (malspam) activity going on. What was the first MAIL FROM address observed in the traffic?
like other questions , we know that the SMTP protocol is involved , so , we can sort by snmp + sort by time in BRIM
_path==”smtp” sort ts cut ts , mailfrom
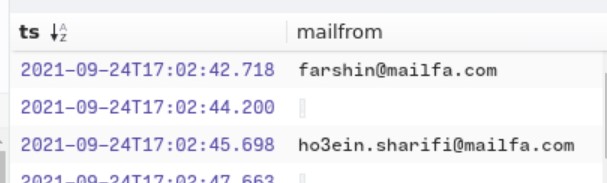
Q19 : How many packets were observed for the SMTP traffic?
To see the number of SMTP packet you need to go to (in wireshark)
statisitic -> protocol hierarchie -> found SMP -> see in the number filed
Awnser: 1439
thank for reading.